You have several devices and you want to receive notifications from your Android phone to your web browser (or vice versa).
Maybe you also want to send notifications via REST API. You are a developer after all. You can think of interesting ways to send notifications.
Pushbullet comes to mind, but you don’t want to sign up with Google or Facebook. You don’t want to use Google services.
Enter Gotify, an open-source notification server for sending and receiving messages.
In this post I will show you how to deploy a Gotify server for free to Heroku.
The free tier has limitations, but for trying out Gotify it’s ideal.
By the end of this tutorial, you will have a fully working notification server with free SSL encryption. It will only take a few minutes!
Prerequisites
You’ll need a free Heroku account, and you should have the Heroku CLI installed on your computer.
Gotify is written in Go, but you don’t need it on your machine.
Here is the architectural overview for Gotify: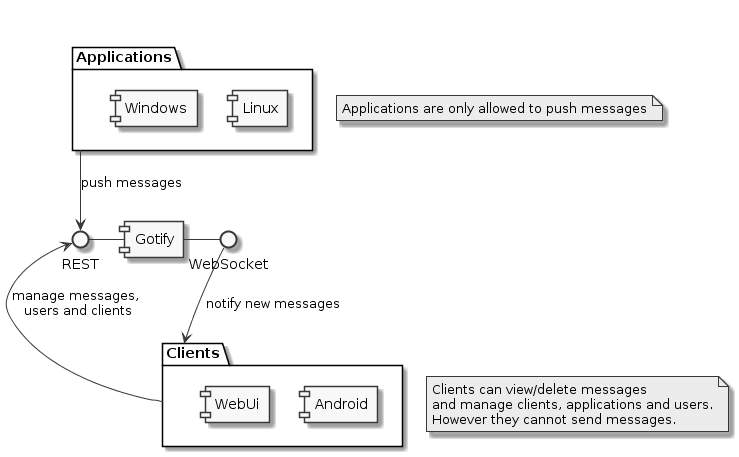 image from the Gotify website
image from the Gotify website
Heroku and Dockhero
Gotify offers a Docker image that we can use.
Unfortunately, you cannot use the usual steps of deploying Docker to Heroku.
Heroku assigns a random port at runtime. There is no way to set that port as an environment variable to the Gotify runtime.
It would be easy if we could configure the Gotify binary with command line flags, but we can’t.
We’ll use Dockhero to work around this problem.
Dockhero is an add-on which turns any Docker image into a microservice attached to your Heroku app.
Guide
Create a new directory for the project.
mkdir gotify-heroku && cd gotify-herokuLogin to Heroku and create a new Heroku app.
heroku login heroku createProvisioning the add-on for Dockhero.
heroku addons:create dockheroInstall CLI plugin for Dockhero.
heroku plugins:install dockheroGenerate sample project:
heroku dh:generate helloworldCreate
dockhero-compose.yml:version: '2' services: app: image: gotify/server environment: - GOTIFY_SERVER_PORT=30100 restart: 'on-failure:10' volumes: - './gotify_data:/app/data' ports: - '80:30100'You can adjust the port to your liking, but you’ll probably need a higher port number. Don’t forget to adjust the
portssettings, too. The first port for the binding should stay80. This is the port that Heroku listens to.Deploy.
heroku dh:compose up -dSee logs.
heroku logs -p dockhero --tailDockhero and Heroku provision a free SSL certificate for you. Get the SSL-encrypted URL.
heroku config:get DOCKHERO_FLEXIBLE_SSL_URLGo the website and change default user and admin.
The default values are both
admin. You should change that.
The web server serves as a client for Gotify. It can receive messages and manage apps, users, and other clients. But it can’t send messages.Add a new application under the “Apps” tab.
For example, you can install the Gotify CLI on your computer and send messages like so:
gotify push "my message"
Android
Gotify has a free Android app.
 image from the Gotify website
image from the Gotify website
The Android app can serve as a Gotify client (receive messages) as well as a Gotify application (send messages).
Chrome-Based Browsers
If you want to send messages from your web browser, you can install an extension: gotify/push.
 image from the gotify-push GitHub repo
image from the gotify-push GitHub repo
The extension needs some additional settings in dockhero-compose.yml:
environment:
- GOTIFY_SERVER_CORS_ALLOWEDORIGINS="- chrome-extension://cbegkpikakpajcaoblfkeindhhikpfmd"
- GOTIFY_SERVER_CORS_ALLOWMETHODS="- \"GET\"\n- \"POST\""
- GOTIFY_SERVER_CORS_ALLOWHEADERS="- \"Authorization\"\n- \"content-type\""
- GOTIFY_SERVER_STREAM_ALLOWEDORIGINS="cbegkpikakpajcaoblfkeindhhikpfmd"
Summary
You’ve now got a free Gotify instance running on Heroku. Wasn’t that easy?